What is LiDAR?
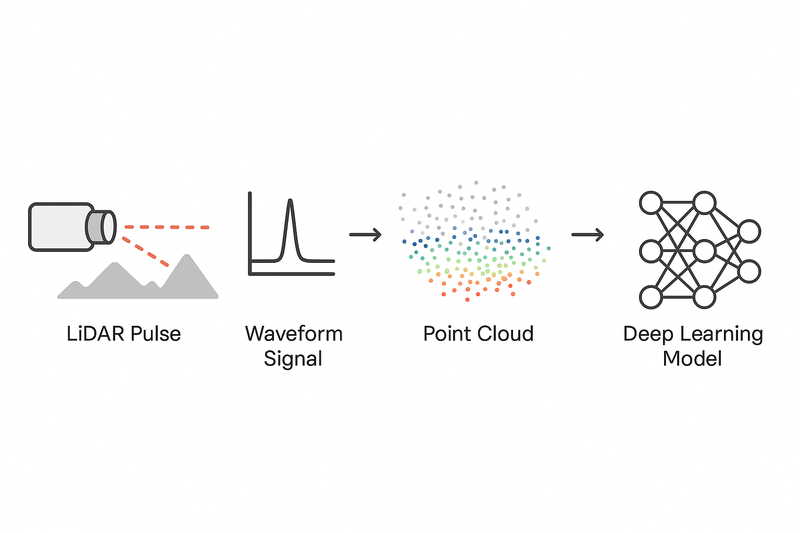
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) measures distances by emitting laser pulses and analyzing their reflections. Each pulse provides:
- Range - distance from time of flight
- Intensity - reflectivity of the surface
- Angle - direction of the laser beam
Millions of these returns create a point cloud - a 3D map with coordinates (x, y, z) and additional attributes.
[if mso & !supportInlineShapes & supportFields]><span style='mso-element:field-begin;mso-field-lock:yes'></span><span style='mso-spacerun:yes'></span>SHAPE <span style='mso-spacerun:yes'></span>\* MERGEFORMAT <span style='mso-element:field-separator'></span><![endif] [if gte vml 1]><v:shapetype id="_x0000_t75" coordsize="21600,21600" o:spt="75" o:preferrelative="t" path="m@4@5l@4@11@9@11@9@5xe" filled="f" stroked="f"> <v:stroke joinstyle="miter"/> <v:formulas> <v:f eqn="if lineDrawn pixelLineWidth 0"/> <v:f eqn="sum @0 1 0"/> <v:f eqn="sum 0 0 @1"/> <v:f eqn="prod @2 1 2"/> <v:f eqn="prod @3 21600 pixelWidth"/> <v:f eqn="prod @3 21600 pixelHeight"/> <v:f eqn="sum @0 0 1"/> <v:f eqn="prod @6 1 2"/> <v:f eqn="prod @7 21600 pixelWidth"/> <v:f eqn="sum @8 21600 0"/> <v:f eqn="prod @7 21600 pixelHeight"/> <v:f eqn="sum @10 21600 0"/> </v:formulas> <v:path o:extrusionok="f" gradientshapeok="t" o:connecttype="rect"/> <o:lock v:ext="edit" aspectratio="t"/> </v:shapetype><![endif] [if mso & !supportInlineShapes & supportFields]><v:shape id="_x0000_i1025" type="#_x0000_t75" style='width:300pt;height:200.4pt'> <v:imagedata croptop="-65520f" cropbottom="65520f"/> </v:shape><span style='mso-element:field-end'></span><![endif]
Data Formats
Discreet Returns: Most common format malfunction key surface hits
[x, y, z, intensity, return_number, timestamp, ring_id]
Storage Formats
- .LAS/.LAZ (geospatial)
- .PCD (robotics)
- .BIN (autonomous driving datasets)
Deep Learning Applications
1. Point-based Networks
- PointNet/PointNet++ - Process raw point coordinates directly
- Used for object classification and segmentation
2. Voxel-based Networks
- VoxelNet/SECOND - Convert points to 3D grids, apply 3D CNNs
- Used for 3D object detection in autonomous vehicles
3. Range/BEV Projections
- Project LiDAR to 2D images or bird's-eye-view grids
- Enable efficient 2D CNN processing
4. Multimodal Fusion
- Combine LiDAR geometry with camera RGB data
- Used in autonomous driving (Tesla FSD, Waymo)
5. Signal Level Processing
- Apply neural networks directly to raw waveform signals
- Preserves more physical detail than point clouds
Conclusion
LiDAR signals form the backbone of modern 3D perception systems. Deep learning transforms these signals from simple distance measurements into rich semantic understanding, enabling machines to perceive and navigate the 3D world with increasing precision and intelligence.


Comments 0
Please sign in to leave a comment.
No comments yet. Be the first to share your thoughts!